
- #Tigervnc debian install#
- #Tigervnc debian full#
- #Tigervnc debian android#
- #Tigervnc debian password#
- #Tigervnc debian download#
#Tigervnc debian install#
Simplest way to get a working graphical environment is to install Fluxbox:
#Tigervnc debian android#
When using Android XServer rather than Android XSDL these are optional. Note that you don't need to set variable "PULSE_SERVER" like application suggests because Termux uses its own Pulseaudio package. The only differences are that you don't have to configure authentication and variable "DISPLAY" should be set like Depending on packages you installed, you may see either entirely black screen or terminal prompt (only if 'aterm' is installed).
#Tigervnc debian password#
You will be prompted for password that you entered on first launch of 'vncserver'.
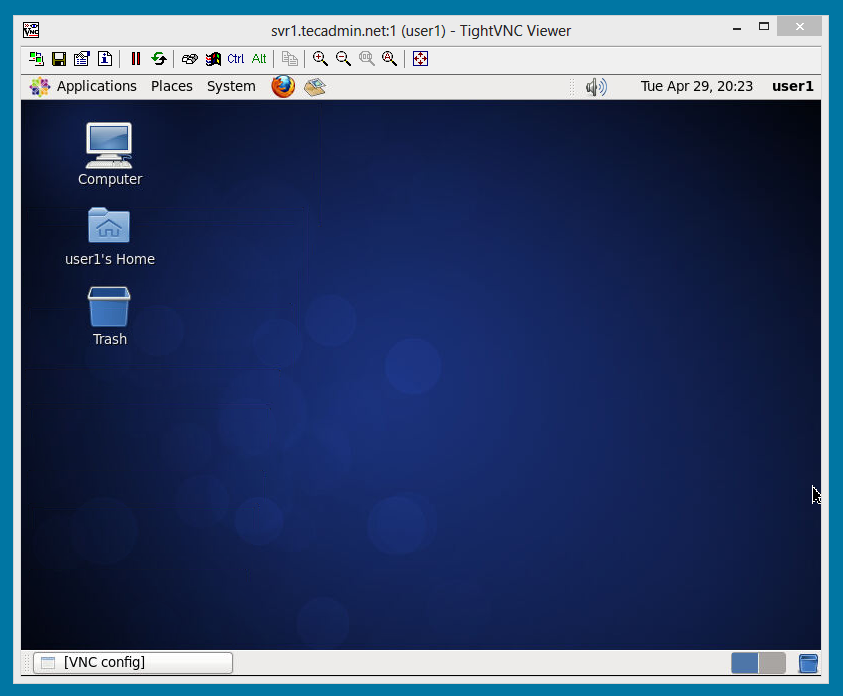

So for display 'localhost:1' the port will be 5901.Ģ. Determine port number on which VNC server listens. Here will be assumed that you use this Android VNC client: VNC Viewer (developed by RealVNC Limited).ġ. You may even put this variable to your bashrc or profile so you don't have to always set it manually unless display address will be changed. Finally, to make programs do graphical output to the display 'localhost:1', set environment variable like shown here (yes, without specifying 'localhost'): It means that X (vnc) server is available on display 'localhost:1'.Ĥ. Log file is /data/data/com.termux/files/home/.vnc/localhost:1.log Starting applications specified in /data/data/com.termux/files/home/.vnc/xstartup New 'localhost:1 ()' desktop is localhost:1Ĭreating default startup script /data/data/com.termux/files/home/.vnc/xstartupĬreating default config /data/data/com.termux/files/home/.vnc/config If everything is okay, you will see this message: Note that passwords are not visible when you are typing them and maximal password length is 8 characters.ģ. Would you like to enter a view-only password (y/n)? n You will require a password to access your desktops. If you decided to use VNC for graphical output, follow these instructions for properly setting up VNC server.Īt first time, you will be prompted for setting up passwords: To disable this repository, you need to uninstall package x11-repo. It will automatically add appropriate sources.list file and PGP key. You can enable it by running the following command:
#Tigervnc debian download#
Here is official download page for TigerVNC:įrom this page, download the latest TigerVNC binary executable file for Linux operating system.X11 packages are available in a separate APT repository. The below mentioned process should work for all popular Linux distributions. Running TigerVNC 1.5 on Linux (Ubuntu, Fedora, CentOS, Debian)
#Tigervnc debian full#
It lets you generate two passwords now, one for full access of the system and other for just “view only” purpose (We will demonstrate this feature later in this article).TigerVNC can now run fine on IPV 6 systems as well.

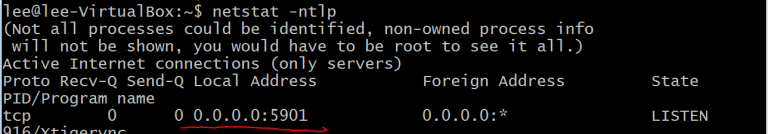
TigerVNC is a well known client/server application, which lets users to communicate with remote computer’s graphical interface.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
